CMS has set up a few requirements to participate in the eRx program. First, EPs must have and use a qualified eRx system and report on his or her adoption and use of the eRx system via a quality code on the claim. Secondly, the EP must meet the criteria for a successful electronic prescriber specified by CMS for a particular reporting period. Finally, at least 10 percent of a successful electronic prescriber’s Medicare Part B covered services must be made up of codes that appear in the denominator of the eRx measure. The last analysis is an important distinction to determine inclusion/exclusion in the program and the ability to achieve an incentive or avoid penalties. The 2013 services included in the denominator of the eRx measure are below.
Denominator criteria (Eligible cases) 2013
Patient visit during the reporting period (CPT or HCPCS): 90791, 90792, 90832, 90834, 90837, 90839, 92002, 92004, 92012, 92014, 96150, 96151, 96152, 99201, 99202, 99203, 99204, 99205, 99211, 99212, 99213, 99214, 99215, 99304, 99305, 99306, 99307, 99308, 99309, 99310, 99315, 99316, 99324, 99325, 99326, 99327, 99328, 99334, 99335, 99336, 99337, 99341, 99342, 99343, 99344, 99345, 99347, 99348, 99349, 99350, G0101, G0108, G0109
E-prescribing instances are similarly reported as PQRS measures are, whereby the quality code goes on the claim with the denominator eligible code from the list above when and if the provider e-prescribes.
All doctors of medicine, osteopathy and podiatric medicine as well as NPPs such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants, among others, are considered EPs, but there are some who are EPs but unable to participate, those being:
- Professionals who provide Part B services, but bill MC at a facility/institutional (Part A) level.
- Professionals must bill Medicare at an individual National Provider Identifier level, where the rendering provider’s individual NPI is entered on CMS-1500 type paper or electronic claims billing, associated with specific line-item services.
- Professionals who reassign benefits to a critical access hospital that bills outpatient services at a facility level, such as CAH Method II billing, cannot participate, since the CAH does not include the individual provider NPI on their Institutional (FI) claims.
- Services payable under fee schedules or methodologies other than the PFS are not included in PQRS or the eRx Incentive Program, for example, services provided in federally qualified health centers, independent diagnostic testing facilities, independent laboratories, hospitals, including method I critical access hospitals, rural health clinics, ambulance providers and ambulatory surgery center facilities.
This means that outside of the relevant entity exclusions above (i.e., IDTs and independent laboratories), most practitioners are considered EPs and therefore could be subject to the incentives and/or adjustments if they do not successfully e-prescribe in accordance with the program requirements.
There are also other considerations to take into account. A majority of hospital-based providers do not bill for many, if any, of the codes in the eRx measure as above. CMS has documented what an EP’s “exclusion criteria” is for applying the 2014 adjustment. For example, those EPs who have less than 10 percent of their total allowed Medicare charges for the first half of 2013 coming from the eRx measure codes, or has less than 100 cases containing an encounter code in the measure above submitted to Medicare in the first half of 2013, will be “excluded” from the e-Rx payment adjustment for 2014.
Many hospital-based practices have minimal, if any, percentage of charges that are attributable to the codes in the eRx measure which is what has “automatically excluded” them from the adjustment. If an analysis of the EP’s six month service offerings concludes that their allowed charges attributable to the encounter codes in the measure hover close to or exceed 10 percent, then the EP should be e-prescribing, reviewing other exclusion criteria, or manually claim an applicable exemption.
Payment adjustment exclusion criteria for individual EPs
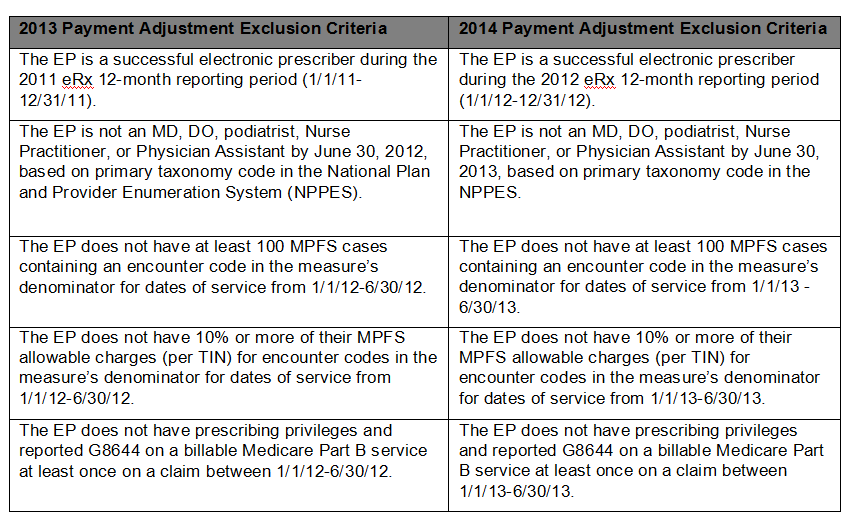
The last year that a provider can achieve an incentive of 0.5 percent of allowed charges if the requirements are met is 2013. The adjustment schedule is below, and the penalties have been in place since the start of 2012:
- -1.0 percent adjustment in 2012 (EP will receive 99 percent of their Medicare Part B PFS amount that would otherwise apply to such services);
- -1.5 percent adjustment in 2013 (EP will receive 98.5 percent of their Medicare Part B PFS amount for covered professional services); and
- -2.0 percent adjustment in 2014 (EP will receive 98 percent of their Medicare Part B PFS amount for covered professional services).
If an EP does not meet the exclusion criteria, then the EP will need to e-prescribe. The adjustment avoidance requirements mandate that the EP will need to report 10 cases of e-prescribing (e.g., the appropriate quality code paired with an encounter code from the e-prescribing measure or other service) on applicable patients over the first half of 2013 to avoid the 2014 adjustment (see table below). Additionally, if the EP wants to achieve the incentive, they must report e-prescribing on 25 patients over the course of the year 2013. Achieving the e-prescribing incentive and avoiding the adjustment has different criteria to meet.
If an EP wants to avoid the 2014 adjustment they must e-prescribe 10 times during the first half of 2013; if the EP met the criteria to obtain the eRx 2012 incentive for e-prescribing they have already avoided the 2014 adjustment. To avoid the adjustment, CMS does allow the reporting of the e-prescribing quality code on any Part B billable service if e-prescribing was performed, and not just when a code from the measure denominator is billed. The EP must be aware that the e-prescribing in that case will not be counted towards the minimum needed for incentive purposes. In other words, if the EP does e-prescribe in the first six months, but not during an encounter that is exemplified by a code in the denominator the EP can apply the quality code and it will count towards the 10 encounters needed to avoid the adjustment, but it will not count towards the 25 encounters needed for the incentive. The e-prescribing event signified by the quality code paired with a code from the denominator is necessary to count towards the incentive requirements.
Reporting options for avoiding the 2014 payment adjustment
IndividualEPs: Six-month reporting period (Dates of Service Jan.1, 2013 to June 30, 2013)
| Reporting Method | Data Processing | Criteria |
| Claims | Data must be processed into the NCH no later than July 26, 2013. | Report G8553 for at least 10 MPFS encounters. The eRx G-code can be reported on any Medicare Part B claim that includes a billable Part B service, regardless of whether the claim contains coding in the eRx measure’s denominator. |
If the provider does not meet the exclusion criteria and for some other reason cannot e-prescribe, CMS has a listing of exemptions that an EP can manually claim to avoid the adjustment, if applicable. Individual EPs requesting a hardship exemption from the 2014 eRx payment adjustment will be able to submit their request for one of the following hardship exemptions via the CMS Quality Reporting Communication Support Page:
- The EP or eRx GPRO practices in an area with limited high-speed Internet access
- The EP or eRx GPRO practices in an area with limited available pharmacies for electronic prescribing
- The EP or eRx GPRO is unable to electronically prescribe due to local, state, or federal law or regulation
- The EP or eRx GPRO has limited prescribing activity, as defined by an EP generating fewer than 100 prescriptions during a six-month reporting period.
Note that CMS will announce when the communication support page becomes available for requesting a hardship exemption for the 2014 eRx payment adjustment.
The following new 2014 eRx payment adjustment exemptions will be determined by CMS through review of the EHR Incentive Program attestation and registration system and will be automatically processed by CMS:
- Those EPs and every member within a group practice participating in eRx GPRO who achieve meaningful use under the Medicare or Medicaid EHR Incentive Program during the 12-month eRx reporting period (Jan. 1, 2012 to Dec. 31, 2012) or the six-month eRx reporting period (Jan. 1, 2013 to June 30, 2013)
- Those EPs and every member within a group practice participating in
- eRx GPRO who demonstrate intent to participate in the Medicare or Medicaid EHR Incentive Program by registering, providing EHR certification ID and adopting certified EHR tecnology by Jan.31, 2013.
CPT copyright 2013 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. CPT is a registered trademark of the American Medical Association.
Missy Lovell, BSN, RN, MBA is the compliance manager with Medical Management Professionals, Inc.
More Articles on ePrescribing:
Electronic Prescribing Initiative to Prevent Medication Errors Grows 33%
AMA Urges Physicians to Apply for E-Prescribing Exemption by Nov. 1
