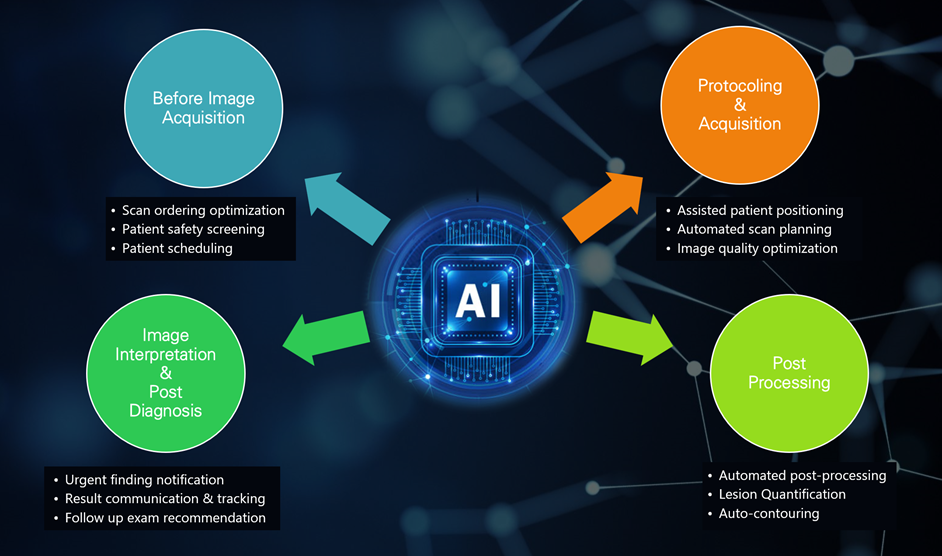
AI for Quality and Efficiency in Radiology
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being leveraged in radiology to enhance image quality and streamline operations. In busy CT and MRI departments, AI innovations help resolve bottlenecks and improve consistency – ultimately delivering a return on investment (ROI) through higher throughput, fewer repeat scans, and better diagnostic outcomes 1. Modern “smart” imaging systems integrate AI from the technologist’s console to image reconstruction and analysis. For example, the new generation of AI-assisted CT scanners can deliver more consistent results, higher image quality, lower radiation dose, and faster throughput, creating extra time for patient-facing tasks2. This article focuses on ready-to-use technology and AI innovations in CT and MRI.
Simplified Technologist Interface
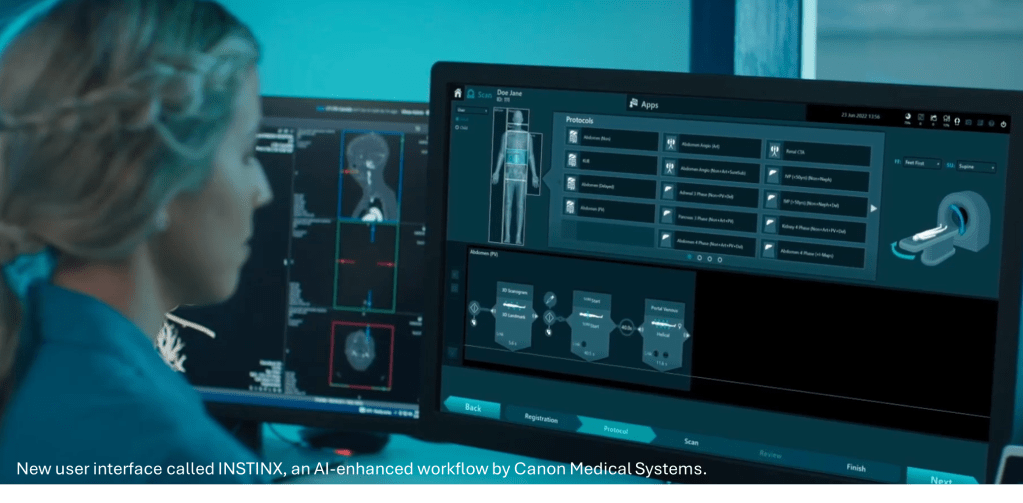
New AI-powered scanner consoles provide an intuitive, guided user experience for technologists. By automating complex settings and workflows, they make advanced scans easier to perform. These innovations have many benefits that include:
- Shorter training time: Ease-of-use means staff learn the system faster, reducing training requirements and onboarding times and associated costs.
- Consistent quality and efficiency: Standardized, step-by-step workflows minimize user variability and errors, ensuring uniform exam quality across technologists. This will also result in higher-quality examinations that can increase diagnostic confidence by the interpreting radiologist. Technologists can work more efficiently and focus on patient care, which boosts throughput.
These innovations help at least partially mitigate challenges related to shortages of technologists and the use of less-experienced technologists for scanning. Freeing up the technologist for patient-facing tasks also improves the consumer (patient) experience.
Automated Patient Positioning & Scan Planning
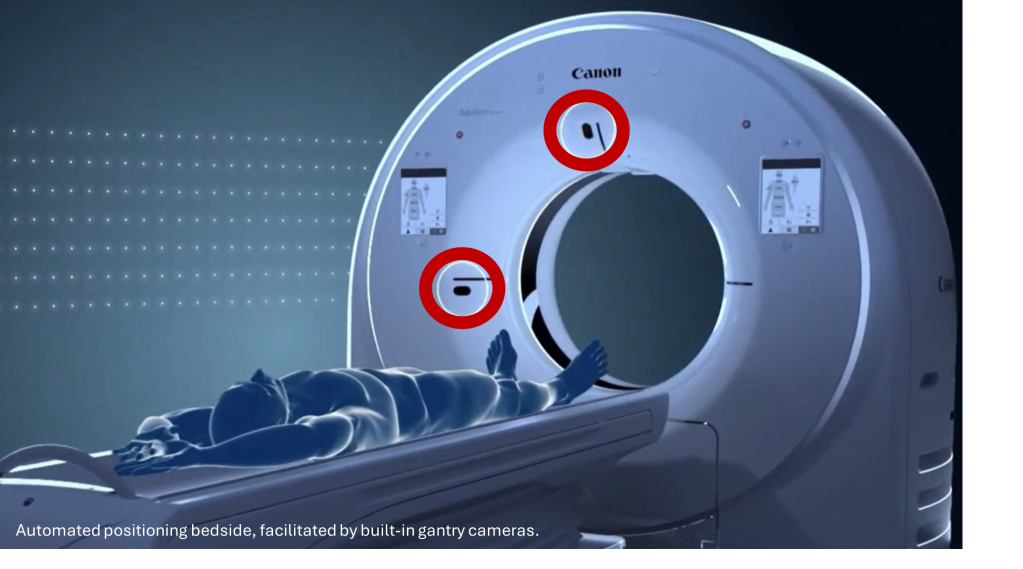
AI-driven auto-positioning uses cameras and deep learning to center patients with a single touch. This innovation enhances patient setup, improving both quality and efficiency3:
- Faster setup: One-touch auto-centering significantly cuts positioning time, speeding up exam preparation and enables higher patient throughput.
- Accurate, repeatable positioning: The system reliably centers the patient (94% within 2 cm of isocenter), optimizing image quality and dose. Consistent positioning also reduced the need for repeat scans due to suboptimal positioning and quality – saving time, radiation, and cost.
- Fast and Accurate Scan Planning: AI-based Anatomical Landmark Detection (ALD) uses 3D Landmark Scan technology to identify key anatomical points and align the scan range with the protocol. This reduces manual guesswork, improves consistency, and saves time.
Similar to the earlier discussion, these innovations help at least partially mitigate challenges related to shortages of technologists and increase overall quality and patient experience.
Deep Learning Reconstruction
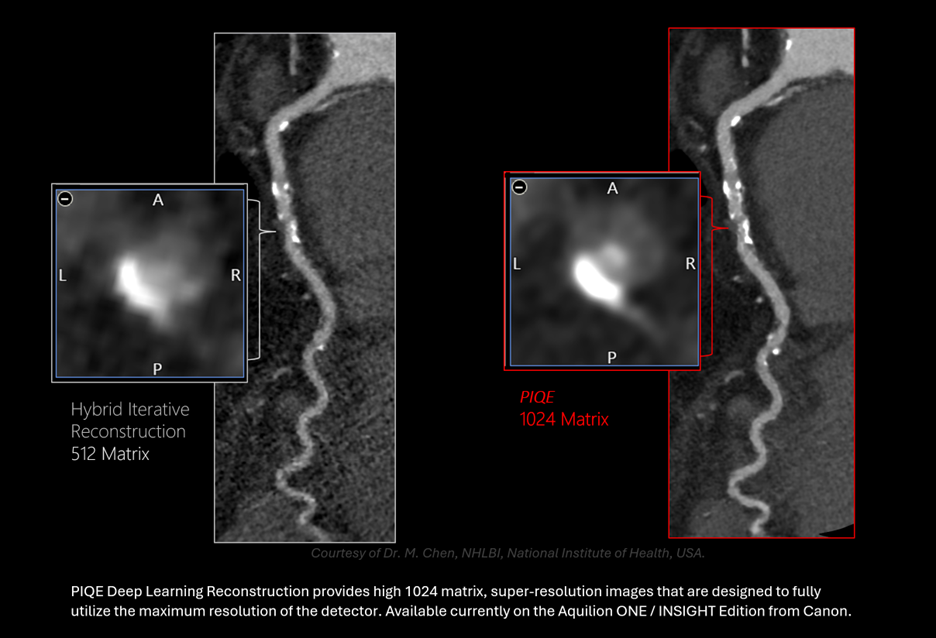
AI-based image reconstruction improves image clarity and can accelerate scanning. In CT, deep learning algorithms can reduce noise and generate higher-quality images at lower radiation doses4. In MRI, in addition to reducing noise and improving quality, they can enable significantly shorter scan times5:
- Improved image quality for both CT and MRI, decreased CT radiation dose: Deep learning reconstructions preserve diagnostic quality even at substantially reduced dose, improving patient safety without sacrificing quality. These can also improve image quality in MRI while reducing scan time.
- Faster MRI scans, higher throughput: Deep learning can significantly speed up MRI sequences, cutting exam times. Shorter scans mean each MRI machine can serve more patients, effectively increasing capacity without added hardware. The faster scan time can improve patient experience and reduce wait times, improving overall consumer experience. This boost in productivity results in a strong return on investment through more exams per day, increasing revenues.
Automated Post-Processing
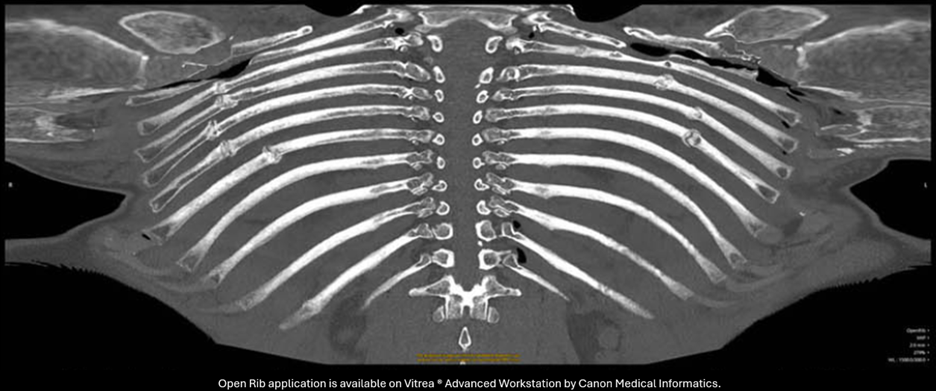
Enhanced technologies, including AI, are increasingly used to automate many post-scan processing tasks, including but not limited to image reformats, that traditionally required manual effort:
- Time savings: Automation of repetitive tasks, such as creating standard views, can result in significant time savings, improving productivity, and freeing up technologists to take care of the patient. This can also improve turn-around-times.
- Standardized outputs and quicker results: Automated post-processing provides consistent, high-quality outputs for every scan. This consistency reduces errors and speeds up diagnosis and reporting, improving patient care and hospital efficiency.
- Fast actionable results: Zero-click workflow streamline study processing, creating fast, actionable results, and delivering time-critical results to the care team.
Conclusion
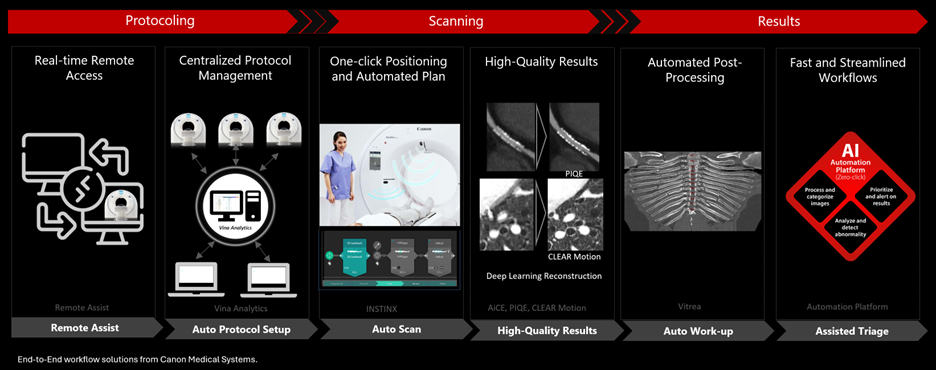
Across CT and MRI imaging, AI technologies are available that enhance operational efficiency, quality, and safety and address operational paint points, including staffing shortages. Simplified interfaces, auto-positioning, deep learning reconstructions, and automated post-processing each contribute to faster workflows and more reliable results. These improvements allow radiology departments to handle higher volumes with existing resources, yielding ROI in the form of increased throughput, fewer repeat scans, and optimized staff utilization – all while elevating the standard of care.
- Pierre K, Haneberg AG, Kwak S, et al. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in the Radiology Roundtrip: Process Streamlining, Workflow Optimization, and Beyond. Semin Roentgenol 2023;58:158-169
- Caballo M, McLennan L, Benbow M, et al. Quantitative evaluation of an artificial intelligence-assisted platform in CT acquisition workflow. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci 2025;57:102133
- Golbus AE, Schuzer JL, Steveson C, et al. Reduced dose helical CT scout imaging on next generation wide volume CT system decreases scan length and overall radiation exposure. Eur J Radiol Open 2024;13:100578
- Kobayashi N, Nakaura T, Yoshida N, et al. Impact of deep learning reconstruction on radiation dose reduction and cancer risk in CT examinations: a real-world clinical analysis. Eur Radiol 2025;35:3499-3507
- Murphy H. Deep learning-based reconstruction nearly halves spinal MRI acquisition times. Radiology Business; 2024
